Maps
Tipping Points Map CGI
The Tipping Points is a critical threshold at which the future state of a system can be qualitatively altered by a small change in forcing1. A tipping element is a part of the Earth system (at least sub-continental in scale) that has a tipping point1. Policy-relevant tipping elements are those that could be forced past a tipping point this century by human activities. Abrupt climate change is the subset of tipping point change which occurs faster than its cause2. Tipping point change also includes transitions that are slower than their cause (in both cases the rate is determined by the system itself). In either case the change in state may be reversible or irreversible. Reversible means that when the forcing is returned below the tipping point the system recovers its original state (either abruptly or gradually). Continue reading
THERMOHALINE CIRCULATION
The Thermohaline circulation is often referred to as the the “Ocean Conveyor Belt” which runs across the planet and influences climate systems far and wide. It has a profound affect on the climate systems in several parts of the world. In a “tipping” scenario, an infux of cold fresh water into the current from increased precipitation and the melt of the Greenland ice-sheet, could cause this current to slow down or shut off. continue reading
SUMMER ASIAN MONSOON
Scientists have predicted that day-to-day rainfall in India might become much more variable during the Asian summer monsoon season due to the growth of the Asian Brown Cloud, the warming Oceans, and lack of fresh drinking water. This may potentially put millions of poor farmers and the country’s agricultural productivity at risk and which is already showing signs of marginal change or upto 15% in oversean.…continure reading
AGULHAS CURRENT
The Agulhas Current is an energetic current driven by the warming Indian oceans, and wind fields resulting from this. It has a profound effect on the European climate, and the coastal climate of South Africa while playing a key role in the global ocean circulation. Until recently little was really known about this small but very important current which now has the attention of oceanographers worldwide.…continue reading
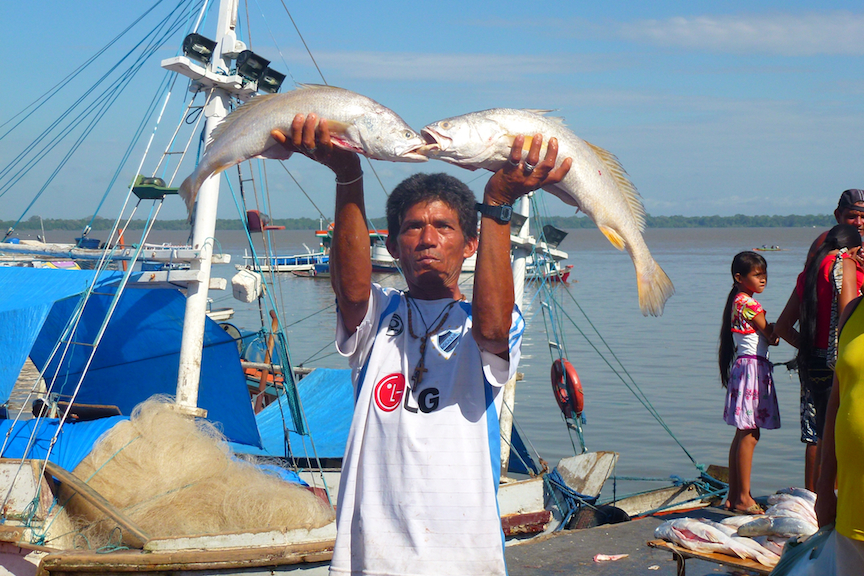
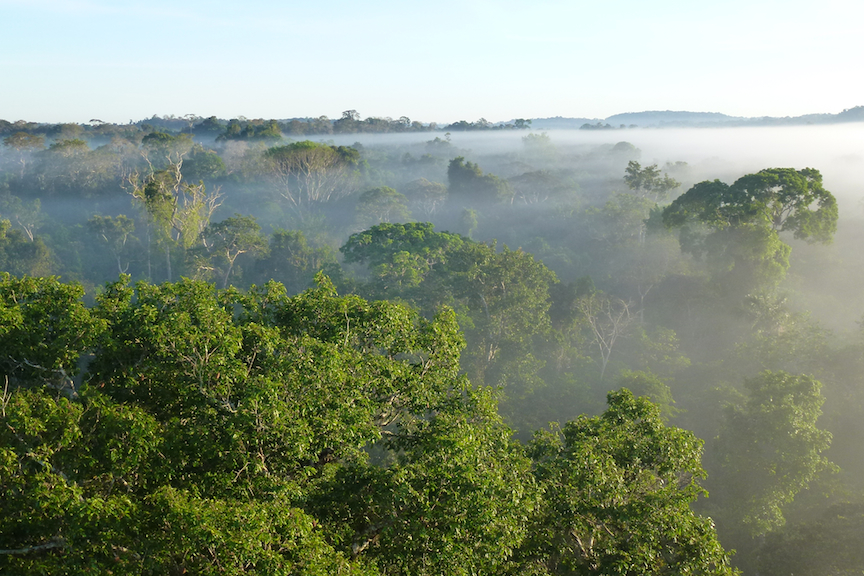
AMAZON DIEBACK
The Amazon rainforest is vulnerable through a combination of human influences, including deforestation, fire and climate change. As the world’s largest store of biodiversity and a major sink for carbon dioxide, the future fate of the Amazon rainforest is of concern to us all. Due to its exceptional biodiversity, around one quarter of all terrestrial species are currently found in the Amazon. The Amazon also represents a major sink for human emissions of carbon dioxide, currently absorbing around 2 billion tons per year. However, this buffer against rising greenhouse gas concentrations is vulnerable, as highlighted by the two major droughts in the past 10 years (in 2005 and 2010).…continue reading
EQUILIBRIUM LINE GREENLAND
Scientists like Prof Alun Hubbard come to S10 camp on the Greenland Icesheet to study ice movement. They are trying to establish just how fast the ice sheet is melting. Twenty years ago, S10 Camp was chosen to be located in a safe zone just above the point the scientists call the equilibrium line. Here, the amount of snowfall and melt each year was equal, making it very stable. But in the last decade, the equilibrium line has started to change and move. Continue reading..