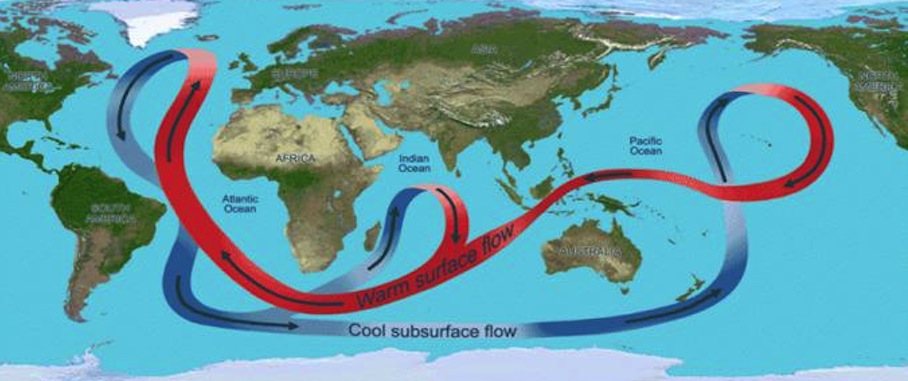
Thermohaline Circulation
The Thermohaline circulation is often referred to as the the “Ocean Conveyor Belt” which runs across the planet and influences climate systems far and wide. It has a profound affect on the climate systems in several parts of the world. In a “tipping” scenario, an infux of cold fresh water into the current from increased precipitation and the melt of the Greenland ice-sheet, could cause this current to slow down or shut off.
This would have a domino effect across the planet: the diluted salty water would loose some of its pushing and plunging energy in a fresh water enviroment. The dilution of the salt content would slow down the performance of the current, and the pace of its movement, slowing down the warm waters it collects as it travels all the way to Europe.
The THC slow down or shut down would cool the Norh Atlantic and warm the South Pacific.The would cause a southward shift of the ITCZ which would drastically effect rainfall in many regions along the equator bring drought, or severe flooding.
Read more on the Thermohaline Circulation – Global Ocean Conveyor System